
前端开发规范
开发规范目录及说明
命名规范
为了让大家书写可维护的代码,而不是一次性的代码
让团队当中其他人看你的代码能一目了然
甚至一段时间时候后你再看你某个时候写的代码也能看
普通变量命名规范
- 命名方法 :驼峰命名法
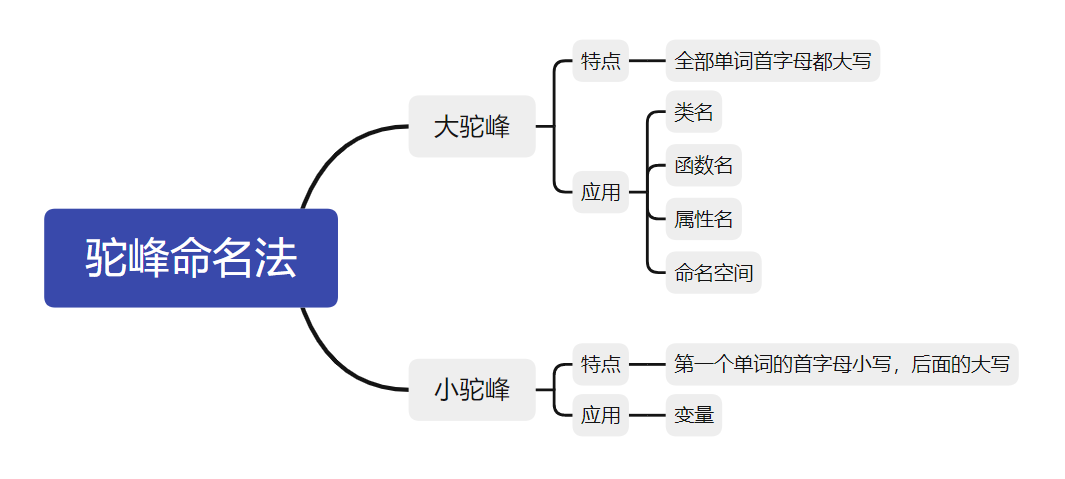
-
命名规范 :
-
命名必须是跟需求的内容相关的词,比如说我想申明一个变量,用来表示我的学校,那么我们可以这样定义
const mySchool = "我的学校"; -
命名是复数的时候需要加s,比如说我想申明一个数组,表示很多人的名字,那么我们可以这样定义
const names = new Array();
-
常量
- 命名方法 : 全部大写
- 命名规范 : 使用大写字母和下划线来组合命名,下划线用以分割单词。
const MAX_COUNT = 10
const URL = 'https://www.baidu.com/'
组件命名规范
官方文档推荐及使用遵循规则:
PascalCase (单词首字母大写命名)是最通用的声明约定
kebab-case (短横线分隔命名) 是最通用的使用约定
-
组件名应该始终是多个单词的,根组件 App 除外
-
有意义的名词、简短、具有可读性
-
命名遵循 PascalCase 约定
-
公用组件以 Abcd (公司名缩写简称) 开头,如(
AbcdDatePicker,AbcdTable) -
页面内部组件以组件模块名简写为开头,Item 为结尾,如(
StaffBenchToChargeItem,StaffBenchAppNotArrItem)
-
-
使用遵循 kebab-case 约定
- 在页面中使用组件需要前后闭合,并以短线分隔,如(
<abcd-date-picker></abcd-date-picker>,<abcd-table></abcd-table>)
- 在页面中使用组件需要前后闭合,并以短线分隔,如(
-
导入及注册组件时,遵循 PascalCase 约定
-
同时还需要注意:必须符合自定义元素规范: 切勿使用保留字。
method 方法命名命名规范
- 驼峰式命名,统一使用动词或者动词+名词形式
//bad
go、nextPage、show、open、login
// good
jumpPage、openCarInfoDialog
- 请求数据方法,以 data 结尾
//bad
takeData、confirmData、getList、postForm
// good
getListData、postFormData
-
init、refresh 单词除外
-
尽量使用常用单词开头(set、get、go、can、has、is)
附: 函数方法常用的动词:
get 获取/set 设置,
add 增加/remove 删除
create 创建/destory 移除
start 启动/stop 停止
open 打开/close 关闭,
read 读取/write 写入
load 载入/save 保存,
create 创建/destroy 销毁
begin 开始/end 结束,
backup 备份/restore 恢复
import 导入/export 导出,
split 分割/merge 合并
inject 注入/extract 提取,
attach 附着/detach 脱离
bind 绑定/separate 分离,
view 查看/browse 浏览
edit 编辑/modify 修改,
select 选取/mark 标记
copy 复制/paste 粘贴,
undo 撤销/redo 重做
insert 插入/delete 移除,
add 加入/append 添加
clean 清理/clear 清除,
index 索引/sort 排序
find 查找/search 搜索,
increase 增加/decrease 减少
play 播放/pause 暂停,
launch 启动/run 运行
compile 编译/execute 执行,
debug 调试/trace 跟踪
observe 观察/listen 监听,
build 构建/publish 发布
input 输入/output 输出,
encode 编码/decode 解码
encrypt 加密/decrypt 解密,
compress 压缩/decompress 解压缩
pack 打包/unpack 解包,
parse 解析/emit 生成
connect 连接/disconnect 断开,
send 发送/receive 接收
download 下载/upload 上传,
refresh 刷新/synchronize 同步
update 更新/revert 复原,
lock 锁定/unlock 解锁
check out 签出/check in 签入,
submit 提交/commit 交付
push 推/pull 拉,
expand 展开/collapse 折叠
begin 起始/end 结束,
start 开始/finish 完成
enter 进入/exit 退出,
abort 放弃/quit 离开
obsolete 废弃/depreciate 废旧,
collect 收集/aggregate 聚集
views 下的文件命名
-
只有一个文件的情况下不会出现文件夹,而是直接放在 views 目录下面,如 index.vue
-
尽量是名词,且使用驼峰命名法
-
开头的单词就是所属模块名字(workbenchIndex、workbenchList、workbenchEdit)
-
名字至少两个单词(good: workbenchIndex)(bad:workbench)
props 命名
在声明 prop 的时候,其命名应该始终使用 camelCase,而在模板中应该始终使用 kebab-case
<!-- bad -->
<script> props: {
'greeting-text': String
} </script>
<welcome-message greetingText="hi"></welcome-message>
<!-- good -->
<script> props: {
greetingText: String
} </script>
<welcome-message greeting-text="hi"></welcome-message>
例外情况
-
作用域不大临时变量可以简写,比如:str,num,bol,obj,fun,arr。
-
循环变量可以简写,比如:i,j,k 等。
结构化规范
目录文件夹及子文件规范
- 以下统一管理处均对应相应模块
- 以下全局文件文件均以 index.js 导出,并在 main.js 中导入
- 以下临时文件,在使用后,接口已经有了,发版后清除
src 源码目录
|-- api 接口,统一管理
|-- assets 静态资源,统一管理
|-- components 公用组件,全局文件
|-- filters 过滤器,全局工具
|-- icons 图标,全局资源
|-- datas 模拟数据,临时存放
|-- lib 外部引用的插件存放及修改文件
|-- mock 模拟接口,临时存放
|-- router 路由,统一管理
|-- store vuex, 统一管理
|-- views 视图目录
| |-- staffWorkbench 视图模块名
| |-- |-- staffWorkbench.vue 模块入口页面
| |-- |-- indexComponents 模块页面级组件文件夹
| |-- |-- components 模块通用组件文件夹
vue 文件基本结构
<template>
<div>
<!--必须在div中编写页面-->
</div>
</template>
<script> export default {
components : {
},
data () {
return {
}
},
mounted() {
},
methods: {
}
} </script>
<!--声明语言,并且添加scoped-->
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>
多个特性的元素规范
多个特性的元素应该分多行撰写,每个特性一行。(增强更易读)
<!-- bad -->
<img src="https://vuejs.org/images/logo.png" alt="Vue Logo">
<my-component foo="a" bar="b" baz="c"></my-component>
<!-- good -->
<img
src="https://vuejs.org/images/logo.png"
alt="Vue Logo"
>
<my-component
foo="a"
bar="b"
baz="c"
>
</my-component>
元素特性的顺序
原生属性放前面,指令放后面
如下所示:
- class
- id,ref
- name
- data-*
- src, for, type, href,value,max-length,max,min,pattern
- title, alt,placeholder
- aria-*, role
- required,readonly,disabled
- is
- v-for
- key
- v-if
- v-else-if
- v-else
- v-show
- v-cloak
- v-pre
- v-once
- v-model
- v-bind,:
- v-on,@
- v-html
- v-text
组件选项顺序
如下所示:
- components
- props
- data
- computed
- created
- mounted
- metods
- filter
- watch
注释规范
代码注释在一个项目的后期维护中显的尤为重要,所以我们要为每一个被复用的组件编写组件使用说明,为组件中每一个方法编写方法说明
务必添加注释列表
-
公共组件使用说明
-
各组件中重要函数或者类说明
-
复杂的业务逻辑处理说明
-
特殊情况的代码处理说明,对于代码中特殊用途的变量、存在临界值、函数中使用的 hack、使用了某种算法或思路等需要进行注释描述
-
多重 if 判断语句
-
注释块必须以
/**(至少两个星号)开头**/ -
单行注释使用//
单行注释
注释单独一行,不要在代码后的同一行内加注释。例如:
bad
var name =”abc”; // 姓名
good
// 姓名
var name = “abc”;
多行注释
组件使用说明,和调用说明
/**
* 组件名称
* @module 组件存放位置
* @desc 组件描述
* @author 组件作者
* @date 2017年12月05日17:22:43
* @param {Object} [title] - 参数说明
* @param {String} [columns] - 参数说明
* @example 调用示例
* <hbTable :title="title" :columns="columns" :tableData="tableData"></hbTable>
**/
编码规范
优秀的项目源码,即使是多人开发,看代码也如出一人之手。统一的编码规范,可使代码更易于阅读,易于理解,易于维护。尽量按照 ESLint 格式要求编写代码
源码风格
使用 ES6 风格编码
-
定义变量使用 let ,定义常量使用 const
-
静态字符串一律使用单引号或反引号,动态字符串使用反引号
// bad
const a = 'foobar'
const b = 'foo' + a + 'bar'
// acceptable
const c = `foobar`
// good
const a = 'foobar'
const b = `foo${a}bar`
const c = 'foobar'
- 解构赋值
- 数组成员对变量赋值时,优先使用解构赋值
// 数组解构赋值
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// bad
const first = arr[0]
const second = arr[1]
// good
const [first, second] = arr
- 函数的参数如果是对象的成员,优先使用解构赋值
// 对象解构赋值
// bad
function getFullName(user) {
const firstName = user.firstName
const lastName = user.lastName
}
// good
function getFullName(obj) {
const { firstName, lastName } = obj
}
// best
function getFullName({ firstName, lastName }) {}
-
拷贝数组
使用扩展运算符(…)拷贝数组。
const items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// bad
const itemsCopy = items
// good
const itemsCopy = [...items]
-
箭头函数
需要使用函数表达式的场合,尽量用箭头函数代替。因为这样更简洁,而且绑定了 this
// bad
const self = this;
const boundMethod = function(...params) {
return method.apply(self, params);
}
// acceptable
const boundMethod = method.bind(this);
// best
const boundMethod = (...params) => method.apply(this, params);
- 模块
- 如果模块只有一个输出值,就使用 export default,如果模块有多个输出值,就不使用 export default,export default 与普通的 export 不要同时使用
// bad
import * as myObject from './importModule'
// good
import myObject from './importModule'
- 如果模块默认输出一个函数,函数名的首字母应该小写。
function makeStyleGuide() {
}
export default makeStyleGuide;
- 如果模块默认输出一个对象,对象名的首字母应该大写。
const StyleGuide = {
es6: {
}
};
export default StyleGuide;
指令规范
- 指令有缩写一律采用缩写形式
// bad
v-bind:class="{'show-left':true}"
v-on:click="getListData"
// good
:class="{'show-left':true}"
@click="getListData"
- v-for 循环必须加上 key 属性,在整个 for 循环中 key 需要唯一
<!-- good -->
<ul>
<li v-for="todo in todos" :key="todo.id">
{ { todo.text } }
</li>
</ul>
<!-- bad -->
<ul>
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{ { todo.text } }
</li>
</ul>
-
避免 v-if 和 v-for 同时用在一个元素上(性能问题)
以下为两种解决方案:
- 将数据替换为一个计算属性,让其返回过滤后的列表
<!-- bad -->
<ul>
<li v-for="user in users" v-if="user.isActive" :key="user.id">
{ { user.name } }
</li>
</ul>
<!-- good -->
<ul>
<li v-for="user in activeUsers" :key="user.id">
{ { user.name } }
</li>
</ul>
<script> computed: {
activeUsers: function () {
return this.users.filter(function (user) {
return user.isActive
})
}
} </script>
- 将 v-if 移动至容器元素上 (比如 ul, ol)
<!-- bad -->
<ul>
<li v-for="user in users" v-if="shouldShowUsers" :key="user.id">
{ { user.name } }
</li>
</ul>
<!-- good -->
<ul v-if="shouldShowUsers">
<li v-for="user in users" :key="user.id">
{ { user.name } }
</li>
</ul>
Props 规范
Props 定义应该尽量详细
// bad 这样做只有开发原型系统时可以接受
props: ['status']
// good
props: {
status: {
type: String,
required: true,
validator: function (value) {
return [
'syncing',
'synced',
'version-conflict',
'error'
].indexOf(value) !== -1
}
}
}
其他
-
避免 this.$parent
-
调试信息 console.log() debugger 使用完及时删除
-
除了三目运算,if,else 等禁止简写
// bad
if (true)
alert(name);
console.log(name);
// bad
if (true)
alert(name);
console.log(name)
// good
if (true) {
alert(name);
}
console.log(name);
CSS 规范
通用规范
-
统一使用"-"连字符
-
省略值为 0 时的单位
// bad
padding-bottom: 0px;
margin: 0em;
// good
padding-bottom: 0;
margin: 0;
-
如果 CSS 可以做到,就不要使用 JS
-
建议并适当缩写值,提高可读性,特殊情况除外
“建议并适当”是因为缩写总是会包含一系列的值,而有时候我们并不希望设置某一值,反而造成了麻烦,那么这时候你可以不缩写,而是分开写。
当然,在一切可以缩写的情况下,请务必缩写,它最大的好处就是节省了字节,便于维护,并使阅读更加一目了然。
// bad
.box{
border-top-style: none;
font-family: palatino, georgia, serif;
font-size: 100%;
line-height: 1.6;
padding-bottom: 2em;
padding-left: 1em;
padding-right: 1em;
padding-top: 0;
}
// good
.box{
border-top: 0;
font: 100%/1.6 palatino, georgia, serif;
padding: 0 1em 2em;
}
- 声明应该按照下表的顺序
左到右,从上到下
| 显示属性 | 自身属性 | 文本属性和其他修饰 |
|---|---|---|
| display | width | font |
| visibility | height | text-align |
| position | margin | text-decoration |
| float | padding | vertical-align |
| clear | border | white-space |
| list-style | overflow | color |
| top | min-width | background |
// bad
.box {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
border: 3px solid #ddd;
left: 30%;
position: absolute;
text-transform: uppercase;
background-color: #eee;
right: 30%;
isplay: block;
font-size: 1.5rem;
overflow: hidden;
padding: 1em;
margin: 1em;
}
// good
.box {
display: block;
position: absolute;
left: 30%;
right: 30%;
overflow: hidden;
margin: 1em;
padding: 1em;
background-color: #eee;
border: 3px solid #ddd;
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
font-size: 1.5rem;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
-
元素选择器应该避免在 scoped 中出现
官方文档说明:在 scoped 样式中,类选择器比元素选择器更好,因为大量使用元素选择器是很慢的。
-
分类的命名方法
使用单个字母加上"-"为前缀
布局(grid)(.g-);
模块(module)(.m-);
元件(unit)(.u-);
功能(function)(.f-);
皮肤(skin)(.s-);
状态(.z-)。
-
统一语义理解和命名
布局(.g-)
| 语义 | 命名 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| 文档 | doc | doc |
| 头部 | head | hd |
| 主体 | body | bd |
| 尾部 | foot | ft |
| 主栏 | main | mn |
| 主栏子容器 | mainc | mnc |
| 侧栏 | side | sd |
| 侧栏子容器 | sidec | sdc |
| 盒容器 | wrap/box | wrap/box |
模块(.m-)、元件(.u-)
| 语义 | 命名 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| 导航 | nav | nav |
| 子导航 | subnav | snav |
| 面包屑 | crumb | crm |
| 菜单 | menu | menu |
| 选项卡 | tab | tab |
| 标题区 | head/title | hd/tt |
| 内容区 | body/content | bd/ct |
| 列表 | list | lst |
| 表格 | table | tb |
| 表单 | form | fm |
| 热点 | hot | hot |
| 排行 | top | top |
| 登录 | login | log |
| 标志 | logo | logo |
| 广告 | advertise | ad |
| 搜索 | search | sch |
| 幻灯 | slide | sld |
| 提示 | tips | tips |
| 帮助 | help | help |
| 新闻 | news | news |
| 下载 | download | dld |
| 注册 | regist | reg |
| 投票 | vote | vote |
| 版权 | copyright | cprt |
| 结果 | result | rst |
| 标题 | title | tt |
| 按钮 | button | btn |
| 输入 | input | ipt |
功能(.f-)
| 语义 | 命名 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| 浮动清除 | clearboth | cb |
| 向左浮动 | floatleft | fl |
| 向右浮动 | floatright | fr |
| 内联块级 | inlineblock | ib |
| 文本居中 | textaligncenter | tac |
| 文本居右 | textalignright | tar |
| 文本居左 | textalignleft | tal |
| 垂直居中 | verticalalignmiddle | vam |
| 溢出隐藏 | overflowhidden | oh |
| 完全消失 | displaynone | dn |
| 字体大小 | fontsize | fs |
| 字体粗细 | fontweight | fw |
皮肤(.s-)
| 语义 | 命名 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| 字体颜色 | fontcolor | fc |
| 背景 | background | bg |
| 背景颜色 | backgroundcolor | bgc |
| 背景图片 | backgroundimage | bgi |
| 背景定位 | backgroundposition | bgp |
| 边框颜色 | bordercolor | bdc |
状态(.z-)
| 语义 | 命名 | 简写 |
|---|---|---|
| 选中 | selected | sel |
| 当前 | current | crt |
| 显示 | show | show |
| 隐藏 | hide | hide |
| 打开 | open | open |
| 关闭 | close | close |
| 出错 | error | err |
| 不可用 | disabled | dis |
sass 规范
-
当使用 Sass 的嵌套功能的时候,重要的是有一个明确的嵌套顺序,以下内容是一个 SCSS 块应具有的顺序。
- 当前选择器的样式属性
- 父级选择器的伪类选择器 (:first-letter, :hover, :active etc)
- 伪类元素 (:before and :after)
- 父级选择器的声明样式 (.selected, .active, .enlarged etc.)
- 用 Sass 的上下文媒体查询
- 子选择器作为最后的部分
.product-teaser {
// 1. Style attributes
display: inline-block;
padding: 1rem;
background-color: whitesmoke;
color: grey;
// 2. Pseudo selectors with parent selector
&:hover {
color: black;
}
// 3. Pseudo elements with parent selector
&:before {
content: "";
display: block;
border-top: 1px solid grey;
}
&:after {
content: "";
display: block;
border-top: 1px solid grey;
}
// 4. State classes with parent selector
&.active {
background-color: pink;
color: red;
// 4.2. Pseuso selector in state class selector
&:hover {
color: darkred;
}
}
// 5. Contextual media queries
@media screen and (max-width: 640px) {
display: block;
font-size: 2em;
}
// 6. Sub selectors
> .content > .title {
font-size: 1.2em;
// 6.5. Contextual media queries in sub selector
@media screen and (max-width: 640px) {
letter-spacing: 0.2em;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
}
}
特殊规范
- 对用页面级组件样式,应该是有作用域的
- 对于公用组件或者全局组件库,我们应该更倾向于选用基于 class 的 BEM 策略
<style lang='scss'></style> // bad
<!-- 使用 scoped 作用域 -->
<style lang='scss' scoped></style> // good
<!-- 使用 BEM 约定 -->
<style> // good
.c-Button {
border: none;
border-radius: 2px;
}
.c-Button--close {
background-color: red;
} </style>
- 感谢你赐予我前进的力量


